In this issue:
Welcome back to your weekly dose of AI news for Life Science!
This week, we have some exciting new models lined up for you:
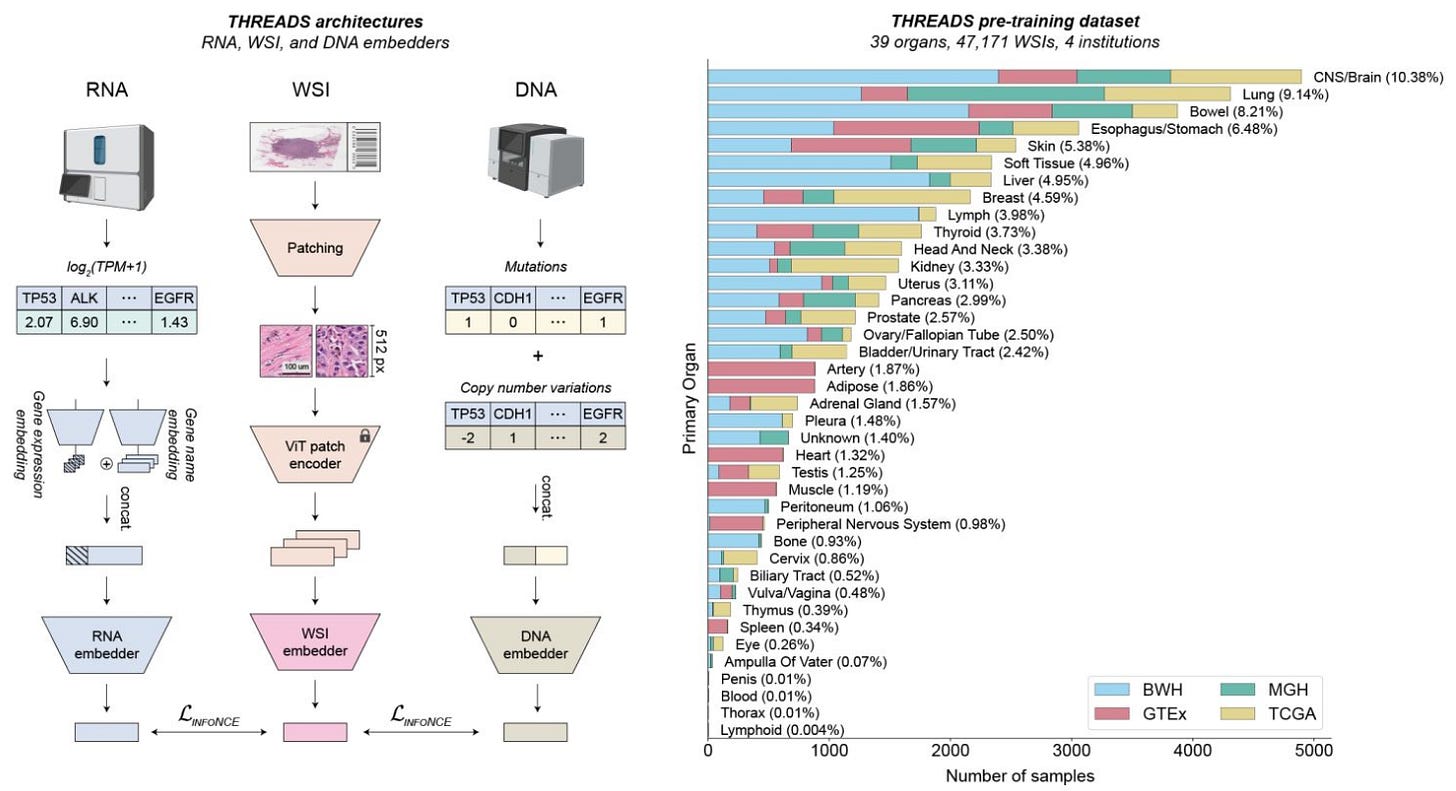
THREADS: a multimodal foundation model for pathology trained on paired histology and genomic data 🔬
BoKDiff: Best-of-K Diffusion for AI-Powered 3D Drug Design 🧬
Dedenser: A Python Package for Clustering and Downsampling Chemical Libraries 💻
Dive into these game-changing innovations and explore how they are transforming the biotech and healthcare landscapes!
THREADS: a multimodal foundation model for pathology trained on paired histology and genomic data 🔬
There has been a lot of new exciting foundation models in pathology such as H-optimus-0 from Bioptimus. Despite these advances, foundation models are still limited in their ability to encode the entire whole-slide images without additional training and often lack complementary multimodal data. Introducing THREADS, a slide-level foundation model capable of generating universal representations of whole-slide images of any size!
📌 Key Insights:
THREADS was pretrained using a multimodal learning approach on a diverse cohort of 47,171 hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained tissue sections,
paired with corresponding genomic and transcriptomic profiles—the largest such paired dataset to be used for foundation model development to date.
THREADS outperformed all baselines in an extensive benchmarking across 54 oncology tasks, including clinical subtyping, grading, mutation prediction, immunohistochemistry status determination, treatment
response prediction and survival prediction
THREADS is particularly well-suited for predicting rare events, further emphasising its clinical utility.
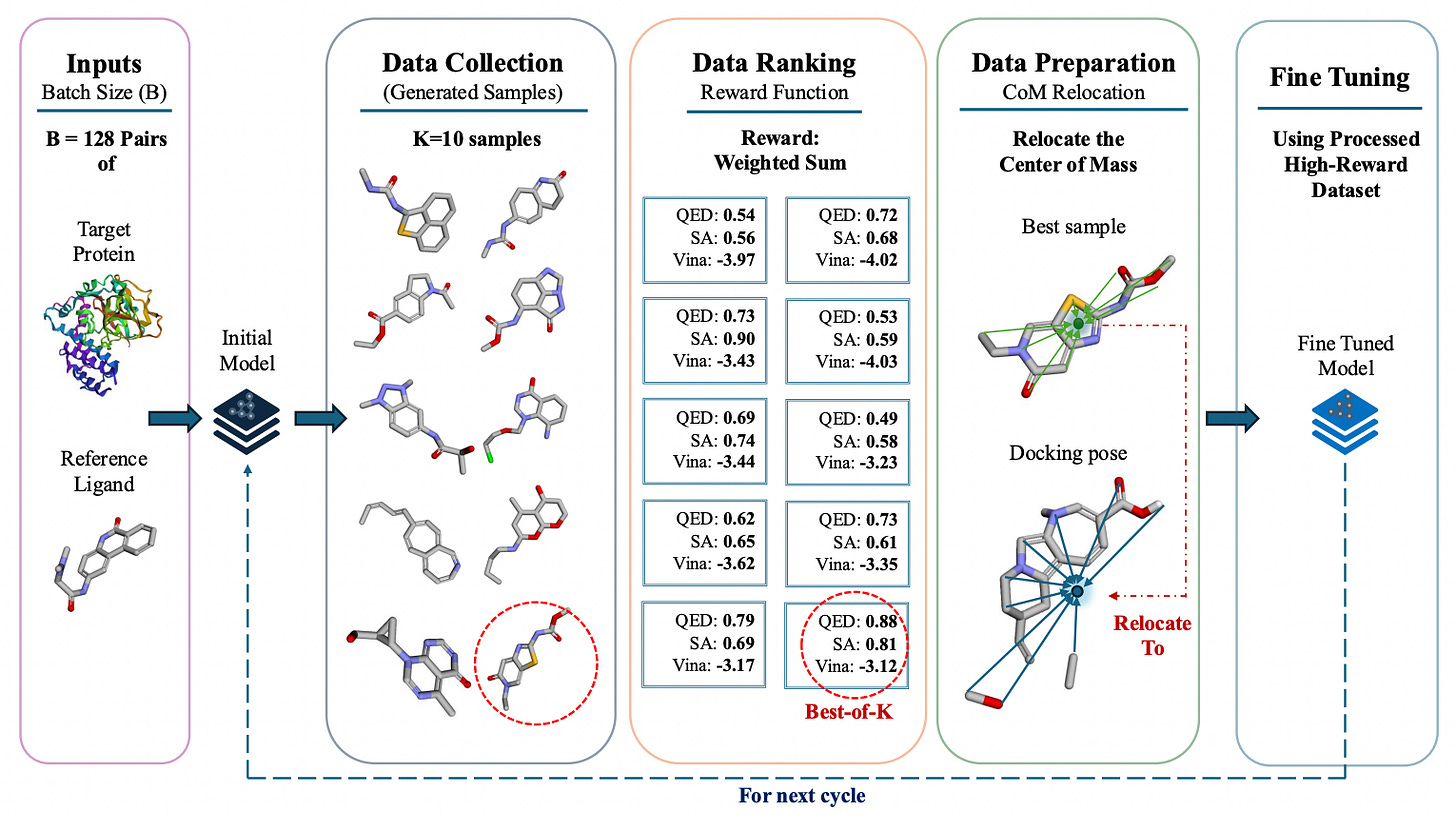
BoKDiff: Best-of-K Diffusion for AI-Powered 3D Drug Design 🧬
A major challenge in AI-driven drug design is ensuring generated molecules align properly with protein binding sites while maintaining drug-like properties. Enter BoKDiff, an innovative Best-of-K diffusion alignment framework designed to refine 3D molecular generation for drug discovery. Developed at the University of Central Florida, BoKDiff enhances molecular docking accuracy by optimizing ligand positioning and structural quality. The method significantly improves drug-likeness (QED) and docking success rates, surpassing existing generative models such as DecompDiff.
📌 Key Insights:
Improved ligand alignment: Uses center-of-mass relocation for better protein-ligand interactions.
Higher success rates: Achieves a 26% success rate in molecular generation on the CrossDocked2020 dataset, outperforming prior models.
Multi-objective optimization: Balances key molecular properties like QED, synthesizability (SA), and docking scores.
Best-of-N sampling approach: Enhances molecule selection without requiring extensive fine-tuning.
Dedenser: A Python Package for Clustering and Downsampling Chemical Libraries 💻
Drug design is a long and complex process, very costly, which includes the screening of vast chemical libraries in order to find promising future drugs. This step is essential and normally a critical cost for preclinical studies. Introducing Dedenser, a Python package devoted to decreasing the number of molecules to test. It uses specific clustering algorithms to select a subset of molecules that best represents the whole chemical space of the full dataset.
📌 Key Insights:
Easy to use (only one line of code after installation)
Saves time in testing molecules by decreasing the number of molecules to test
Promising downsampling results on the ZINC database and an Aryl Bromides database
Did you find this newsletter insightful? Share it with a colleague!
Subscribe Now to stay at the forefront of AI in Life Science.
Connect With Us
Have questions or suggestions? We'd love to hear from you!
📧 Email Us | 📲 Follow on LinkedIn | 🌐 Visit Our Website